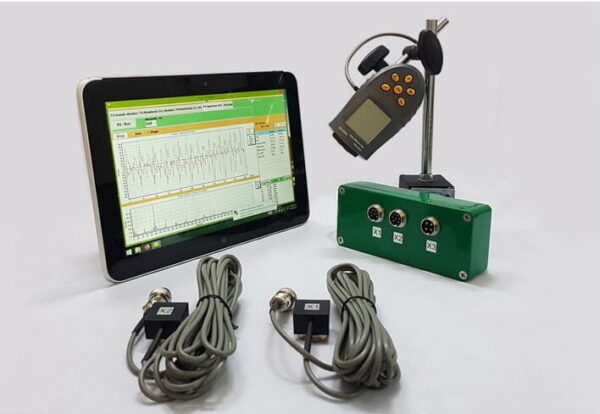
Pengimbang mudah alih & Penganalisis getaran Balanset-1A
$2,390.24
The Balanset-1A is equipped with 2 channels and is designed for dynamic balancing in two planes. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including crushers, fans, mulchers, augers on combines, shafts, centrifuges, turbines, and many others. Its versatility Read more
Fan Balancing
(Maklumat yang digunakan daripada ISO 31350-2007 VIBRATION. KIPAS INDUSTRI. KEPERLUAN UNTUK KUALITI GETARAN DAN PENGIMBANG YANG DIHASILKAN)
Getaran yang dihasilkan oleh kipas adalah salah satu ciri teknikalnya yang paling penting. Ia menunjukkan kualiti reka bentuk dan pembuatan produk. Peningkatan getaran mungkin menunjukkan pemasangan kipas yang tidak betul, kemerosotan keadaan teknikalnya, dsb. Atas sebab ini, getaran kipas biasanya diukur semasa ujian penerimaan, semasa pemasangan sebelum pentauliahan, serta semasa menjalankan program pemantauan keadaan mesin. Data getaran kipas juga digunakan dalam reka bentuk sokongan dan sistem yang disambungkan (saluran). Pengukuran getaran biasanya dilakukan dengan port sedutan dan pelepasan terbuka, tetapi harus diperhatikan bahawa getaran kipas boleh berbeza dengan ketara dengan perubahan dalam aerodinamik aliran udara, kelajuan putaran dan ciri-ciri lain.
ISO 10816-1-97, ISO 10816-3-2002 dan ISO 31351-2007 mewujudkan kaedah pengukuran dan menentukan lokasi penderia getaran. Jika pengukuran getaran dijalankan untuk menilai kesannya pada saluran atau tapak kipas, titik pengukuran dipilih dengan sewajarnya.
Pengukuran getaran kipas boleh menjadi mahal, dan kadangkala kosnya jauh melebihi kos pembuatan produk itu sendiri. Oleh itu, sebarang sekatan pada nilai komponen getaran diskret individu atau parameter getaran dalam jalur frekuensi hanya perlu diperkenalkan apabila melebihi nilai ini menunjukkan kerosakan kipas. Bilangan titik pengukuran getaran juga harus dihadkan berdasarkan tujuan penggunaan hasil pengukuran. Biasanya, adalah mencukupi untuk mengukur getaran pada penyokong kipas untuk menilai keadaan getaran kipas.
Tapak adalah tempat kipas dipasang dan apa yang menyediakan sokongan yang diperlukan untuk kipas. Jisim dan kekakuan tapak dipilih untuk mengelakkan penguatan getaran yang dihantar melaluinya.
Sokongan terdiri daripada dua jenis:
- sokongan patuh: Sistem sokongan kipas direka supaya frekuensi semula jadi pertama sokongan adalah jauh lebih rendah daripada frekuensi putaran operasi kipas. Apabila menentukan tahap pematuhan sokongan, sisipan elastik antara kipas dan struktur sokongan harus dipertimbangkan. Pematuhan sokongan dipastikan dengan menggantung kipas pada spring atau meletakkan sokongan pada elemen elastik (spring, pengasing getah, dsb.). Kekerapan semula jadi sistem gantungan – kipas biasanya kurang daripada 25% daripada frekuensi yang sepadan dengan kelajuan putaran minimum kipas yang diuji.
- sokongan tegar: Sistem sokongan kipas direka supaya frekuensi semula jadi pertama sokongan adalah lebih tinggi daripada frekuensi putaran operasi. Kekakuan tapak kipas adalah relatif. Ia harus dipertimbangkan berbanding dengan kekakuan galas mesin. Nisbah getaran perumahan galas kepada getaran asas mencirikan pengaruh pematuhan asas. Tapak boleh dianggap tegar dan cukup besar jika amplitud getaran tapak (dalam mana-mana arah) berhampiran kaki mesin atau rangka sokongan adalah kurang daripada 25% daripada hasil pengukuran getaran maksimum yang diperoleh pada sokongan galas terdekat (dalam sebarang arah).
Oleh kerana jisim dan kekakuan tapak sementara di mana kipas dipasang semasa ujian kilang mungkin berbeza dengan ketara daripada keadaan pemasangan di tapak operasi, nilai had keadaan kilang digunakan untuk getaran jalur sempit dalam julat frekuensi putaran, dan untuk ujian kipas di tapak – kepada getaran jalur lebar, menentukan keadaan getaran keseluruhan mesin. Tapak operasi ialah lokasi pemasangan akhir kipas, yang mana keadaan operasi ditentukan.
Kategori Peminat (kategori BV)
Peminat dikategorikan berdasarkan ciri penggunaan yang dimaksudkan, kelas ketepatan mengimbangi dan nilai had parameter getaran yang disyorkan. Reka bentuk dan tujuan kipas adalah kriteria yang membenarkan mengklasifikasikan banyak jenis kipas mengikut nilai ketidakseimbangan yang boleh diterima dan tahap getaran (kategori BV).
Jadual 1 membentangkan kategori yang boleh dikaitkan dengan kipas berdasarkan keadaan aplikasinya, dengan mengambil kira nilai ketidakseimbangan yang dibenarkan dan tahap getaran. Kategori kipas ditentukan oleh pengilang.
Jadual 1 – Kategori Peminat
| Syarat Permohonan | Contoh | Penggunaan Kuasa, kW | BV-kategori |
| Ruang Kediaman dan Pejabat | Kipas Siling dan Loteng, Penghawa Dingin Tingkap | ≤ 0.15 | BV-1 |
| > 0.15 | BV-2 | ||
| Bangunan dan Premis Pertanian | Kipas untuk Sistem Pengudaraan dan Penyaman Udara; Peminat dalam Peralatan Siri | ≤ 3.7 | BV-2 |
| > 3.7 | BV-3 | ||
| Proses Perindustrian dan Penjanaan Kuasa | Kipas di Ruang Tertutup, Lombong, Penghantar, Dandang, Terowong Angin, Sistem Pembersihan Gas | ≤ 300 | BV-3 |
| > 300 | lihat ISO 10816-3 | ||
| Pengangkutan, termasuk Kapal Laut | Peminat Lokomotif, Lori dan Kereta | ≤ 15 | BV-3 |
| > 15 | BV-4 | ||
| Terowong | Peminat untuk Pengudaraan Kereta Api Bawah Tanah, Terowong, Garaj | ≤ 75 | BV-3 |
| > 75 | BV-4 | ||
| mana-mana | BV-4 | ||
| Pengeluaran Petrokimia | Peminat untuk Membuang Gas Berbahaya, dan Digunakan dalam Proses Teknologi Lain | ≤ 37 | BV-3 |
| > 37 | BV-4 | ||
| Computer Chip Production | Fans for Creating Clean Rooms | mana-mana | BV-5 |
| Notes
1 This standard only considers fans with power less than 300 kW. The vibration assessment of fans with greater power is according to ISO 10816-3. However, standard series electric motors can have a rated power of up to 355 kW. Fans with such electric motors should be accepted according to this standard.
2 Table 1 does not apply to large diameter (usually from 2800 to 12500 mm) low-speed light axial fans used in heat exchangers, cooling towers, etc. The balancing accuracy class for such fans should be G16, and the fan category – BV-3
|
|||
When purchasing individual rotor elements (wheels or impellers) for subsequent installation on the fan, the balancing accuracy class of these elements (see table 2) should be followed, and when purchasing the fan as a whole, the results of factory vibration tests (table 4) and on-site vibration (table 5) should also be considered. Usually, these characteristics are agreed upon, so the choice of fan can be made based on its BV-category.
The category established in table 1 is typical for the normal use of fans, but in justified cases, the customer may request a fan of a different BV-category. It is recommended to specify the fan’s BV-category, balancing accuracy class, and acceptable vibration levels in the equipment supply contract.
A separate agreement between the customer and the manufacturer can be concluded regarding the fan installation conditions, so that the factory testing of the assembled fan considers the planned installation conditions at the operating site. In the absence of such an agreement, there are no restrictions on the type of base (rigid or compliant) for factory tests.
Fan Balancing
General Provisions
The fan manufacturer is responsible for balancing the fans according to the relevant regulatory document. This standard is based on the requirements of ISO 1940-1. Balancing is usually carried out on highly sensitive, specially designed balancing machines, allowing for an accurate assessment of residual imbalance.
Fan Balancing Accuracy Classes
The balancing accuracy classes for fan wheels are applied in accordance with table 2. The fan manufacturer can perform balancing for several elements in assembly, which may include, in addition to the wheel, the shaft, coupling, pulley, etc. In addition, individual assembly elements may require balancing.
Table 2 – Balancing Accuracy Classes
|
Fan Category
|
Rotor (Wheel) Balancing Accuracy Class
|
|
BV-1
|
G16
|
|
BV-2
|
G16
|
|
BV-3
|
G6.3
|
|
BV-4
|
G2.5
|
|
BV-5
|
G1.0
|
|
Note: Fans of category BV-1 can include small size fans weighing less than 224 g, for which it is difficult to maintain the specified balancing accuracy. In this case, the uniformity of mass distribution relative to the fan’s axis of rotation should be ensured by the manufacturing technology.
|
|
Fan Vibration Measurement
Measurement Requirements
General Provisions
Figures 1 – 4 show some possible measurement points and directions on each fan bearing. The values given in table 4 relate to measurements in the direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation. The number and location of measurement points for both factory tests and on-site measurements are determined at the manufacturer’s discretion or by agreement with the customer. It is recommended to measure on the bearings of the fan wheel shaft (impeller). If this is not possible, the sensor should be installed in a place where the shortest mechanical connection between it and the bearing is ensured. The sensor should not be mounted on unsupported panels, the fan housing, enclosure elements, or other places not directly connected to the bearing (such measurement results can be used, but not for assessing the fan’s vibrational state, but for obtaining information about the vibration transmitted to the duct or base – see ISO 31351 and ISO 5348.
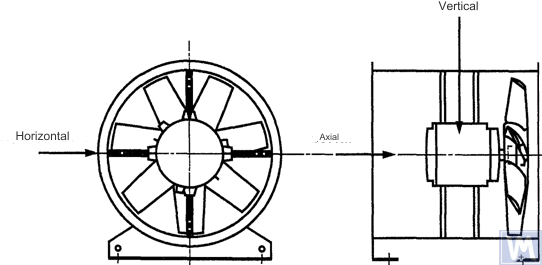
Figure 1. Location of a three-coordinate sensor for a horizontally mounted axial fan
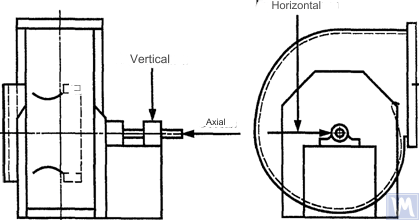
Figure 2. Location of a three-coordinate sensor for a single-suction radial fan
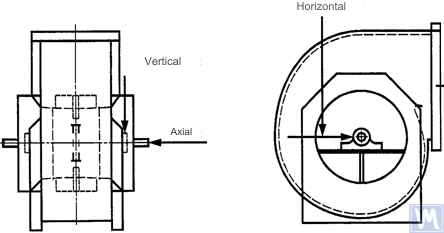
Figure 3. Location of a three-coordinate sensor for a double-suction radial fan
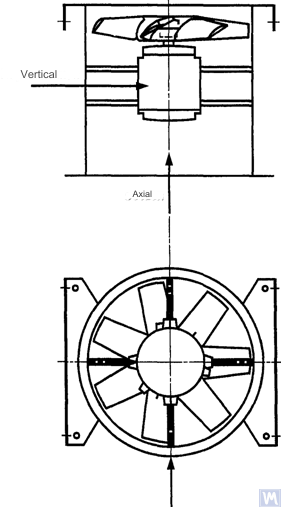
Figure 4. Location of a three-coordinate sensor for a vertically mounted axial fan
Measurements in the horizontal direction should be carried out at a right angle to the shaft axis. Measurements in the vertical direction should be carried out at a right angle to the horizontal measurement direction and perpendicular to the fan shaft. Measurements in the longitudinal direction should be carried out parallel to the shaft axis.
Measurements using inertia-type sensors
All vibration values specified in this standard refer to measurements taken using inertia-type sensors, the signal of which reproduces the movement of the bearing housing.
The sensors used can be either accelerometers or velocity sensors. Particular attention should be paid to the correct attachment of sensors: without gaps on the support surface, without swings and resonances. The size and mass of the sensors and the attachment system should not be excessively large to avoid significant changes in the measured vibration. The total error caused by the method of sensor attachment and calibration of the measuring system should not exceed +/- 10% of the measured value.
Measurements using non-contact sensors
By agreement between the user and the manufacturer, requirements for the maximum allowable shaft displacement (see ISO 7919-1) within sliding bearings may be established. The corresponding measurements can be carried out using non-contact sensors.
In this case, the measuring system determines the displacement of the shaft surface relative to the bearing housing. It is obvious that the allowable amplitude of displacements should not exceed the value of the bearing clearance. The clearance value depends on the size and type of bearing, the load (radial or axial), and the measurement direction (some bearing designs have an elliptical hole, for which the clearance in the horizontal direction is greater than in the vertical direction). The variety of factors that need to be considered does not allow setting uniform shaft displacement limits, but some recommendations are presented in table 3. The values given in this table represent a percentage of the total radial clearance value in the bearing in each direction.
Table 3 – Maximum Relative Shaft Displacement within the Bearing
| Fan Vibrational State | Maximum Recommended Displacement, Percentage of Clearance Value (Along Any Axis) |
| Commissioning/Satisfactory State | Less than 25% |
| Warning | +50% |
| Shutdown | +70% |
| 1) Radial and axial clearance values for a specific bearing should be obtained from its supplier. | |
The given values take into account “false” displacements of the shaft surface. These “false” displacements appear in the measurement results because, in addition to the shaft vibration, mechanical runouts also affect these results if the shaft is bent or has an out-of-round shape. When using a non-contact sensor, the measurement results will also include electrical runouts determined by the magnetic and electrical properties of the shaft material at the measurement point. It is believed that during the commissioning and subsequent normal operation of the fan, the range of the sum of mechanical and electrical runouts at the measurement point should not exceed the larger of two values: 0.0125 mm or 25% of the measured displacement value. Runouts are determined by slowly rotating the shaft (at a speed of 25 to 400 rpm), when the effect of forces caused by imbalance on the rotor is negligible. To meet the established runout tolerance, additional shaft machining may be required. Non-contact sensors should, if possible, be mounted directly on the bearing housing.
The given limit values apply only to a fan operating in its nominal mode. If the fan design allows operation with variable rotational speed, higher vibration levels are possible at other speeds due to the inevitable influence of resonances.
If the fan design allows changing the blade positions relative to the airflow at the intake port, the given values should be applied for conditions with the blades fully open. It should be noted that airflow stall, especially noticeable at large blade angles relative to the intake airflow, can lead to increased vibration levels.
Fan Support System
The vibrational state of fans after installation is determined considering the support stiffness. A support is considered rigid if the first natural frequency of the “fan – support” system exceeds the rotational speed. Usually, when mounted on large concrete foundations, the support can be considered rigid, and when mounted on vibration isolators – compliant. A steel frame, often used for mounting fans, can belong to either of the two support types. In case of doubt about the fan support type, calculations or tests can be carried out to determine the system’s first natural frequency. In some cases, the fan support should be considered rigid in one direction and compliant in another.
Limits of Allowable Fan Vibration during Factory Tests
The limit vibration levels given in table 4 apply to assembled fans. They relate to narrow-band vibration velocity measurements at bearing supports for the rotational frequency used during factory tests.
Jadual 4 – Hadkan Nilai Getaran semasa Ujian Kilang
| Fan Category | Hadkan Halaju Getaran RMS, mm/s | |
| Sokongan Tegar | Sokongan Patuh | |
| BV-1 | 9.0 | 11.2 |
| BV-2 | 3.5 | 5.6 |
| BV-3 | 2.8 | 3.5 |
| BV-4 | 1.8 | 2.8 |
| BV-5 | 1.4 | 1.8 |
| Notes
1 Peraturan untuk menukar unit halaju getaran kepada unit sesaran atau pecutan untuk getaran jalur sempit dinyatakan dalam Lampiran A.
2 Nilai dalam jadual ini digunakan pada beban nominal dan kekerapan putaran nominal kipas yang beroperasi dalam mod dengan bilah pemandu masuk terbuka. Nilai had untuk syarat pemuatan lain harus dipersetujui antara pengilang dan pelanggan, tetapi adalah disyorkan bahawa mereka tidak melebihi nilai jadual lebih daripada 1.6 kali.
|
||
Had Getaran Kipas Yang Dibenarkan semasa Ujian Di Tapak
Getaran mana-mana kipas di tapak operasi bergantung bukan sahaja pada kualiti pengimbangannya. Faktor yang berkaitan dengan pemasangan, seperti jisim dan kekakuan sistem sokongan, juga akan mempunyai pengaruh. Oleh itu, pengeluar kipas tidak bertanggungjawab ke atas tahap getaran kipas di tapak operasinya melainkan ia dinyatakan dalam kontrak.
Jadual 5 menyediakan nilai had yang disyorkan (dalam unit halaju getaran untuk getaran jalur lebar pada perumah galas) untuk operasi normal kipas dalam pelbagai kategori.
Jadual 5 – Hadkan Nilai Getaran di Tapak Operasi
| Fan Vibrational State | Fan Category | Hadkan Halaju Getaran RMS, mm/s | |
| Sokongan Tegar | Sokongan Patuh | ||
| Pentauliahan | BV-1 | 10 | 11.2 |
| BV-2 | 5.6 | 9.0 | |
| BV-3 | 4.5 | 6.3 | |
| BV-4 | 2.8 | 4.5 | |
| BV-5 | 1.8 | 2.8 | |
| Warning | BV-1 | 10.6 | 14.0 |
| BV-2 | 9.0 | 14.0 | |
| BV-3 | 7.1 | 11.8 | |
| BV-4 | 4.5 | 7.1 | |
| BV-5 | 4.0 | 5.6 | |
| Shutdown | BV-1 | __1) | __1) |
| BV-2 | __1) | __1) | |
| BV-3 | 9.0 | 12.5 | |
| BV-4 | 7.1 | 11.2 | |
| BV-5 | 5.6 | 7.1 | |
| 1) Tahap penutupan untuk peminat kategori BV-1 dan BV-2 ditetapkan berdasarkan analisis jangka panjang hasil pengukuran getaran. | |||
Getaran peminat baharu yang ditauliahkan tidak boleh melebihi tahap "pentauliahan". Apabila kipas beroperasi, tahap getarannya dijangka meningkat disebabkan oleh proses haus dan kesan kumulatif faktor yang mempengaruhi. Peningkatan getaran sedemikian secara amnya adalah semula jadi dan tidak sepatutnya menimbulkan kebimbangan sehingga ia mencapai tahap "amaran".
Apabila mencapai tahap getaran "amaran", adalah perlu untuk menyiasat punca peningkatan getaran dan menentukan langkah untuk mengurangkannya. Operasi kipas di negeri ini harus berada di bawah pemantauan berterusan dan terhad kepada masa yang diperlukan untuk mengenal pasti langkah-langkah untuk menghapuskan punca peningkatan getaran.
Sekiranya tahap getaran mencapai tahap "pematikan", langkah-langkah untuk menghapuskan punca peningkatan getaran mesti diambil dengan segera, jika tidak, kipas harus dihentikan. Menangguhkan tahap getaran ke tahap yang boleh diterima boleh menyebabkan kerosakan galas, keretakan pada pemutar, dan pada titik kimpalan perumah kipas, akhirnya mengakibatkan kemusnahan kipas.
Apabila menilai keadaan getaran kipas, adalah penting untuk memantau perubahan dalam tahap getaran dari semasa ke semasa. Perubahan mendadak dalam tahap getaran menunjukkan keperluan untuk pemeriksaan dan langkah penyelenggaraan kipas segera. Apabila memantau perubahan getaran, proses peralihan yang disebabkan oleh, contohnya, penggantian pelincir atau prosedur penyelenggaraan tidak boleh dipertimbangkan.
Pengaruh Prosedur Perhimpunan
Selain roda, kipas menyertakan elemen berputar lain yang boleh menjejaskan tahap getaran kipas: takal pemacu, tali pinggang, gandingan, pemutar motor atau peranti pemacu lain. Jika syarat pesanan memerlukan bekalan kipas tanpa peranti pemacu, mungkin tidak praktikal bagi pengilang untuk menjalankan ujian pemasangan untuk menentukan tahap getaran. Dalam kes sedemikian, walaupun pengeluar telah mengimbangi roda kipas, tidak ada kepastian bahawa kipas akan berjalan lancar sehingga aci kipas disambungkan ke pemacu dan keseluruhan mesin diuji untuk getaran semasa pentauliahan.
Biasanya, selepas pemasangan, pengimbangan tambahan diperlukan untuk mengurangkan tahap getaran ke tahap yang boleh diterima. Untuk semua peminat baharu kategori BV-3, BV-4 dan BV-5, adalah disyorkan untuk mengukur getaran untuk mesin yang dipasang sebelum pentauliahan. Ini akan mewujudkan garis asas dan menggariskan langkah penyelenggaraan selanjutnya.
Pengeluar kipas tidak bertanggungjawab terhadap kesan ke atas getaran bahagian pemacu yang dipasang selepas ujian kilang.
Alat Pengukuran dan Penentukuran Getaran
Alat Pengukuran
Alat ukuran dan mesin pengimbang yang digunakan mesti disahkan dan memenuhi keperluan tugas. Selang antara pengesahan ditentukan oleh cadangan pengilang untuk alat pengukuran (ujian). Keadaan alat ukuran mesti memastikan operasi normalnya sepanjang tempoh ujian.
Kakitangan yang bekerja dengan alat ukuran mesti mempunyai kemahiran dan pengalaman yang mencukupi untuk mengesan potensi kerosakan dan kemerosotan kualiti alat pengukuran.
Penentukuran
Semua alat ukuran mesti ditentukur mengikut piawaian. Kerumitan prosedur penentukuran mungkin berbeza daripada pemeriksaan fizikal yang mudah kepada penentukuran keseluruhan sistem. Jisim pembetulan yang digunakan untuk menentukan ketidakseimbangan baki mengikut ISO 1940-1 juga boleh digunakan untuk menentukur alat ukuran.
Dokumentasi
Balancing
Atas permintaan, jika diperuntukkan oleh syarat kontrak, laporan ujian pengimbangan kipas boleh diberikan kepada pelanggan, yang disyorkan untuk memasukkan maklumat berikut:
– Nama pengeluar mesin pengimbang, nombor model;
– Jenis pemasangan rotor: antara penyokong atau julur;
– Kaedah pengimbangan: statik atau dinamik;
– Jisim bahagian berputar pemasangan rotor;
– Ketidakseimbangan baki dalam setiap satah pembetulan;
– Ketidakseimbangan baki yang dibenarkan dalam setiap satah pembetulan;
– Kelas ketepatan mengimbangi;
– Kriteria penerimaan: diterima/ditolak;
– Sijil pengimbangan (jika perlu).
– Nama pengeluar mesin pengimbang, nombor model;
– Jenis pemasangan rotor: antara penyokong atau julur;
– Kaedah pengimbangan: statik atau dinamik;
– Jisim bahagian berputar pemasangan rotor;
– Ketidakseimbangan baki dalam setiap satah pembetulan;
– Ketidakseimbangan baki yang dibenarkan dalam setiap satah pembetulan;
– Kelas ketepatan mengimbangi;
– Kriteria penerimaan: diterima/ditolak;
– Sijil pengimbangan (jika perlu).
Vibration
Atas permintaan, jika diperuntukkan oleh syarat kontrak, laporan ujian getaran kipas boleh diberikan kepada pelanggan, yang disyorkan untuk memasukkan maklumat berikut:
– Alat ukuran yang digunakan;
– Kaedah lampiran sensor getaran;
– Parameter operasi kipas (aliran udara, tekanan, kuasa);
– Kekerapan putaran kipas;
– Jenis sokongan: tegar atau patuh;
- Getaran yang diukur:
1) Kedudukan sensor getaran dan paksi ukuran,
2) Unit ukuran dan tahap rujukan getaran,
3) Julat kekerapan pengukuran (jalur frekuensi sempit atau luas);
– Tahap getaran yang dibenarkan;
– Tahap getaran yang diukur;
– Kriteria penerimaan: diterima/ditolak;
– Sijil tahap getaran (jika perlu).
– Alat ukuran yang digunakan;
– Kaedah lampiran sensor getaran;
– Parameter operasi kipas (aliran udara, tekanan, kuasa);
– Kekerapan putaran kipas;
– Jenis sokongan: tegar atau patuh;
- Getaran yang diukur:
1) Kedudukan sensor getaran dan paksi ukuran,
2) Unit ukuran dan tahap rujukan getaran,
3) Julat kekerapan pengukuran (jalur frekuensi sempit atau luas);
– Tahap getaran yang dibenarkan;
– Tahap getaran yang diukur;
– Kriteria penerimaan: diterima/ditolak;
– Sijil tahap getaran (jika perlu).
METHODS OF BALANCING FANS ON A BALANCING MACHINE
B.1. Direct Drive Fan
B.1.1. General Provisions
The fan wheel, which is mounted directly on the motor shaft during assembly, should be balanced according to the same rule for accounting for the keyway effect as for the motor shaft.
Motors from previous years of production could be balanced using a full keyway. Currently, motor shafts are balanced using a half-keyway, as prescribed by ISO 31322, and marked with the letter H (see ISO 31322).
B.1.2. Motors Balanced with a Full Keyway
The fan wheel, mounted on the motor shaft balanced with a full keyway, should be balanced without a key on a tapered arbor.
B.1.3. Motors Balanced with a Half-Keyway
For the fan wheel mounted on the motor shaft balanced with a half-keyway, the following options are possible:
a) if the wheel has a steel hub, cut a keyway in it after balancing;
b) balance on a tapered arbor with a half-key inserted into the keyway;
c) balance on an arbor with one or more keyways (see B.3), using full keys.
a) if the wheel has a steel hub, cut a keyway in it after balancing;
b) balance on a tapered arbor with a half-key inserted into the keyway;
c) balance on an arbor with one or more keyways (see B.3), using full keys.
B.2. Fans Driven by Another Shaft
Where possible, all rotating elements, including the fan shaft and pulley, should be balanced as a single unit. If this is impractical, balancing should be performed on an arbor (see B.3) using the same keyway accounting rule as for the shaft.
B.3. Arbor
The arbor on which the fan wheel is mounted during balancing must meet the following requirements:
a) be as light as possible;
b) be in a balanced state, ensured by appropriate maintenance and regular inspections;
c) preferably be tapered to reduce errors associated with eccentricity, resulting from the tolerances of the hub hole and arbor dimensions. If the arbor is tapered, the true position of the correction planes relative to the bearings should be considered in the imbalance calculations.
a) be as light as possible;
b) be in a balanced state, ensured by appropriate maintenance and regular inspections;
c) preferably be tapered to reduce errors associated with eccentricity, resulting from the tolerances of the hub hole and arbor dimensions. If the arbor is tapered, the true position of the correction planes relative to the bearings should be considered in the imbalance calculations.
If it is necessary to use a cylindrical arbor, it should have a keyway cut into it, into which a full key is inserted to transmit the torque from the arbor to the fan wheel.
Another option is to cut two keyways on opposite ends of the shaft diameter, allowing the use of the reverse balancing method. This method involves the following steps. First, measure the wheel imbalance by inserting a full key into one keyway and a half-key into the other. Then rotate the wheel 180° relative to the arbor and measure its imbalance again. The difference between the two imbalance values is due to the residual imbalance of the arbor and the universal drive joint. To obtain the true rotor imbalance value, take half the difference of these two measurements.
SOURCES OF FAN VIBRATION
There are many sources of vibration within the fan, and vibration at certain frequencies can be directly linked to specific design features of the machine. This appendix only covers the most common vibration sources observed in most types of fans. The general rule is that any looseness in the support system causes deterioration in the fan’s vibrational state.
Fan Imbalance
This is the primary source of fan vibration; it is characterized by the presence of a vibration component at the rotational frequency (first harmonic). The cause of imbalance is that the axis of the rotating mass is eccentric or angled to the axis of rotation. This can be caused by uneven mass distribution, the sum of tolerances on the dimensions of the hub hole and shaft, shaft bending, or a combination of these factors. Vibration caused by imbalance mainly acts in the radial direction.
Temporary shaft bending can result from uneven mechanical heating – due to friction between rotating and stationary elements – or electrical nature. Permanent bending can result from changes in material properties or misalignment of the shaft and fan wheel when the fan and motor are separately mounted.
During operation, the fan wheel imbalance can increase due to particle deposition from the air. When operating in an aggressive environment, imbalance can result from uneven erosion or corrosion of the wheel.
Imbalance can be corrected by additional balancing in the appropriate planes, but before performing the balancing procedure, the sources of imbalance should be identified, eliminated, and the machine’s vibrational stability checked.
Fan and Motor Misalignment
This defect can occur when the motor and fan shafts are connected via a belt drive or flexible coupling. Misalignment can sometimes be identified by characteristic vibration frequency components, usually the first and second harmonics of the rotational frequency. In the case of parallel misalignment of the shafts, vibration primarily occurs in the radial direction, while if the shafts intersect at an angle, longitudinal vibration may become dominant.
If the shafts are connected at an angle and rigid couplings are used, alternating forces begin to act in the machine, causing increased wear of the shafts and couplings. This effect can be significantly reduced by using flexible couplings.
Fan Vibration Due to Aerodynamic Excitation
Vibration excitation can be caused by the interaction of the fan wheel with stationary elements of the design, such as guide vanes, motor, or bearing supports, incorrect gap values, or improperly designed air intake and exhaust structures. A characteristic feature of these sources is the occurrence of periodic vibration associated with the wheel’s rotational frequency, against the background of random fluctuations in the interaction of the wheel blades with the air. Vibration can be observed at the blade frequency harmonics, which is the product of the wheel’s rotational frequency and the number of wheel blades.
Aerodynamic instability of the airflow, caused by its stall from the blade surface and subsequent vortex formation, causes broadband vibration, the spectrum shape of which changes depending on the fan’s load.
Aerodynamic noise is characterized by the fact that it is not related to the wheel’s rotational frequency and can occur at subharmonics of the rotational frequency (i.e., at frequencies below the rotational frequency). In this case, significant vibration of the fan housing and ducts can be observed.
If the aerodynamic system of the fan is poorly matched with its characteristics, sharp impacts may occur in it. These impacts are easily distinguishable by ear and are transmitted as impulses to the fan support system.
If the above-mentioned causes lead to blade vibration, its nature can be investigated by installing sensors in different parts of the structure.
Fan Vibration Due to Whirl in the Oil Layer
Whirls that may occur in the lubrication layer of sliding bearings are observed at a characteristic frequency slightly below the rotor’s rotational frequency unless the fan operates at a speed exceeding the first critical. In the latter case, oil wedge instability will be observed at the first critical speed, and sometimes this effect is called resonant whirl.
Sources of Electrical Nature Fan Vibration
Uneven heating of the motor rotor can cause it to bend, leading to imbalance (manifesting at the first harmonic).
In the case of an asynchronous motor, the presence of a component at a frequency equal to the rotational frequency multiplied by the number of rotor plates indicates defects related to the stator plates, and vice versa, components at a frequency equal to the rotational frequency multiplied by the number of rotor plates indicate defects related to the rotor plates.
Many vibration components of electrical nature are characterized by their immediate disappearance when the power supply is turned off.
Fan Vibration Due to Belt Drive Excitation
Generally, there are two types of problems related to belt drives: when the drive’s operation is influenced by external defects and when the defects are in the belt itself.
In the first case, although the belt vibrates, this is due to forcing forces from other sources, so replacing the belt will not produce the desired results. Common sources of such forces are imbalance in the drive system, pulley eccentricity, misalignment, and loosened mechanical connections. Therefore, before changing the belts, vibration analysis should be carried out to identify the excitation source.
If the belts respond to external forcing forces, their vibration frequency will most likely be the same as the excitation frequency. In this case, the excitation frequency can be determined using a stroboscopic lamp, adjusting it so that the belt appears stationary in the lamp’s light.
In the case of a multi-belt drive, unequal belt tension can lead to a significant increase in the transmitted vibration.
Cases where the vibration sources are the belts themselves are related to their physical defects: cracks, hard and soft spots, dirt on the belt surface, missing material from its surface, etc. For V-belts, changes in their width will cause the belt to ride up and down the pulley track, creating vibration due to changing its tension.
If the vibration source is the belt itself, the vibration frequencies are usually the harmonics of the belt’s rotational frequency. In a specific case, the excitation frequency will depend on the nature of the defect and the number of pulleys, including tensioners.
In some cases, the vibration amplitude may be unstable. This is especially true for multi-belt drives.
Mechanical and electrical defects are sources of vibration, which subsequently convert into airborne noise. Mechanical noise can be associated with fan or motor imbalance, bearing noise, axis alignment, duct wall and housing panel vibrations, damper blade vibrations, blade, damper, pipe, and support vibrations, as well as transmission of mechanical vibrations through the structure. Electrical noise is related to various forms of electrical energy conversion: 1) Magnetic forces are determined by the magnetic flux density, the number and shape of the poles, and the geometry of the air gap; 2) Random electrical noise is determined by brushes, arcing, electrical sparks, etc.
Aerodynamic noise can be associated with vortex formation, pressure pulsations, air resistance, etc., and can have both broadband and narrowband nature. Broadband noise can be caused by: a) blades, dampers, and other obstacles in the airflow path; b) fan rotation as a whole, belts, slits, etc.; c) sudden changes in airflow direction or duct cross-section, differences in flow velocities, flow separation due to boundary effects, flow compression effects, etc. Narrowband noise can be caused by: a) resonances (organ pipe effect, string vibrations, panel, structural element vibrations, etc.); b) vortex formation on sharp edges (air column excitation); c) rotations (siren effect, slits, holes, slots on rotating parts).
Impacts created by contact between various mechanical elements of the structure produce noise similar to that produced by a hammer blow, thunder roll, resonating empty box, etc. Impact sounds can be heard from gear teeth impacts and defective belt claps. Impact impulses can be so fleeting that to distinguish periodic impact impulses from transient processes, special high-speed recording equipment is needed. The area where many impact impulses occur, the superimposition of their peaks creates a constant hum effect.
Dependence of Vibration on Fan Support Type
The correct choice of fan support or foundation design is necessary for its smooth, trouble-free operation. To ensure the alignment of rotating components when installing the fan, motor, and other drive devices, a steel frame or reinforced concrete base is used. Sometimes an attempt to save on support construction leads to the inability to maintain the required alignment of the machine components. This is especially unacceptable when vibration is sensitive to alignment changes, particularly for machines consisting of separate parts connected by metal fasteners.
The foundation on which the base is laid can also influence the fan and motor vibration. If the foundation’s natural frequency is close to the fan or motor’s rotational frequency, the foundation will resonate during fan operation. This can be detected by measuring vibration at several points across the foundation, surrounding floor, and fan supports. Often in resonance conditions, the vertical vibration component significantly exceeds the horizontal one. Vibration can be dampened by making the foundation stiffer or increasing its mass. Even if imbalance and misalignment are eliminated, allowing to reduce forcing forces, significant vibration preconditions may still exist. This means that if the fan, together with its support, is close to resonance, achieving acceptable vibration values will require more precise balancing and more accurate shaft alignment than typically required for such machines. This situation is undesirable and should be avoided by increasing the support or concrete block’s mass and/or stiffness.
Vibration Condition Monitoring and Diagnostics Guide
The main principle of machine vibration condition monitoring (hereinafter referred to as the condition) is to observe the results of properly planned measurements to identify a trend of increasing vibration levels and consider it from the perspective of potential problems. Monitoring is applicable in situations where damage develops slowly, and the mechanism’s condition deterioration manifests through measurable physical signs.
Fan vibration, resulting from the development of physical defects, can be monitored at certain intervals, and when an increase in vibration level is detected, the observation frequency can be increased, and a detailed condition analysis can be conducted. In this case, the causes of vibration changes can be identified based on vibration frequency analysis, which allows determining the necessary measures and planning their implementation long before the damage becomes severe. Usually, measures are considered necessary when the vibration level increases by 1.6 times or by 4 dB compared to the baseline level.
The condition monitoring program consists of several stages, which can be briefly formulated as follows:
a) identify the fan’s condition and determine the baseline vibration level (it may differ from the level obtained during factory tests due to different installation methods, etc.);
b) select vibration measurement points;
c) determine the observation (measurement) frequency;
d) establish the information registration procedure;
e) determine the criteria for assessing the fan’s vibrational state, limit values for absolute vibration and vibration changes, summarize the experience of operating similar machines.
a) identify the fan’s condition and determine the baseline vibration level (it may differ from the level obtained during factory tests due to different installation methods, etc.);
b) select vibration measurement points;
c) determine the observation (measurement) frequency;
d) establish the information registration procedure;
e) determine the criteria for assessing the fan’s vibrational state, limit values for absolute vibration and vibration changes, summarize the experience of operating similar machines.
Since fans typically operate without any problems at speeds not approaching the critical, the vibration level should not significantly change with slight speed or load changes, but it is important to note that when the fan operates with variable rotational speed, the established vibration limit values apply to the maximum operating rotational speed. If the maximum rotational speed cannot be reached within the established vibration limit, this may indicate the presence of a serious problem and require a special investigation.
Some diagnostic recommendations provided in Appendix C are based on fan operation experience and are intended for sequential application when analyzing the causes of increased vibration.
To qualitatively assess the vibration of a specific fan and determine guidelines for further actions, the vibration condition zone boundaries established by ISO 10816-1 can be used.
It is expected that for new fans, their vibration levels will be below the limit values given in table 3. These values correspond to the boundary of zone A of the vibration condition according to ISO 10816-1. Recommended values for warning and shutdown levels are established based on the analysis of information collected on specific types of fans.
COMPLIANCE INFORMATION
REFERENCE INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS USED AS NORMATIVE REFERENCES IN THIS STANDARD
Table H.1
|
Designation of the Reference Interstate Standard
|
Designation and Title of the Reference International Standard and the Conditional Designation of Its Degree of Compliance with the Reference Interstate Standard
|
|
ISO 1940-1-2007
|
ISO 1940-1:1986. Vibration. Requirements for the Balancing Quality of Rigid Rotors. Part 1. Determination of Allowable Imbalance (IDT)
|
|
ISO 5348-2002
|
ISO 5348:1999. Vibration and Shock. Mechanical Mounting of Accelerometers (IDT)
|
|
ISO 7919-1-2002
|
ISO 7919-1:1996. Vibration of Non-Reciprocating Machines. Measurements on Rotating Shafts and Criteria for Evaluation. Part 1. General Guidelines (IDT)
|
|
ISO 10816-1-97
|
ISO 10816-1:1995. Vibration. Evaluation of Machine Condition by Vibration Measurements on Non-Rotating Parts. Part 1. General Guidelines (IDT)
|
|
ISO 10816-3-2002
|
ISO 10816-3:1998. Vibration. Evaluation of Machine Condition by Vibration Measurements on Non-Rotating Parts. Part 3. Industrial Machines with a Nominal Power of More Than 15 kW and Nominal Speeds of 120 to 15000 rpm, in-Situ Measurements (IDT)
|
|
ISO 10921-90
|
ISO 5801:1997. Industrial Fans. Performance Testing Using Standardized Ducts (NEQ)
|
|
ISO 19534-74
|
ISO 1925:2001. Vibration. Balancing. Vocabulary (NEQ)
|
|
ISO 24346-80
|
ISO 2041:1990. Vibration and Shock. Vocabulary (NEQ)
|
|
ISO 31322-2006 (ISO 8821:1989)
|
ISO 8821:1989. Vibration. Balancing. Guidelines for Accounting for the Keyway Effect When Balancing Shafts and Fitted Parts (MOD)
|
|
ISO 31351-2007 (ISO 14695:2003)
|
ISO 14695:2003. Industrial Fans. Vibration Measurement Methods (MOD)
|
|
Note: The following conditional designations of the standard’s compliance degree are used in this table: IDT – identical standards;
|
|

0 Komen